Architecture & Installation
This section provides information about the architecture of the solutions and how to install it.
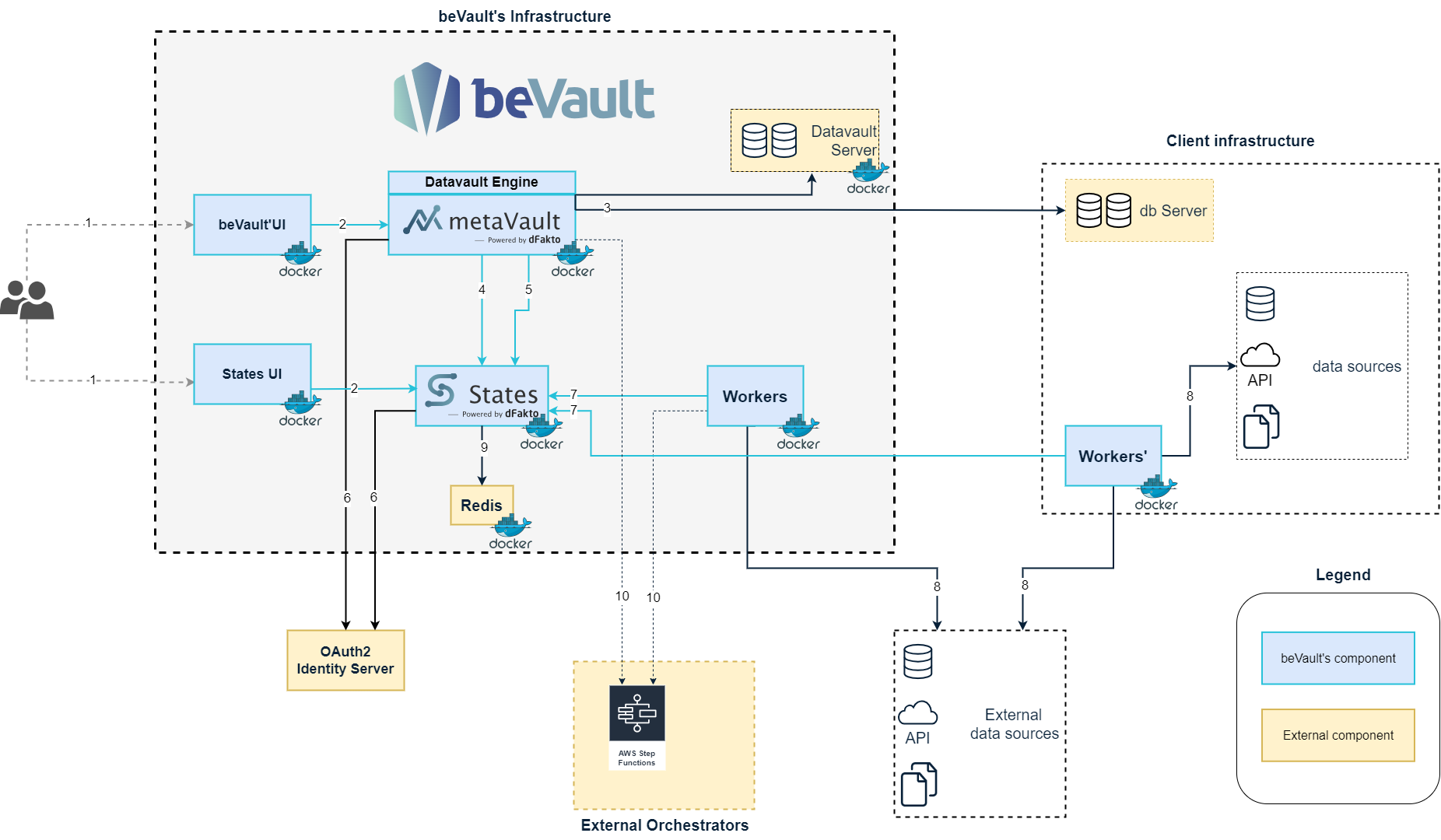
beVault’s Components
| Component | Summary | Current version |
|---|---|---|
| Metavault | This is the main application of the dataFactory. It allows users to create a project in which they will design a Data Vault. The queries generated by the embedded SQL engine are certified by the Data Vault Alliance with the VTCP. It currently supports PostgreSQL, SQL Server, Snowflake and IBM db2 | 5.0.0 |
| metaVault UI | This is the user interface of beVault. For the moment, it only allows the users to interact with metavault but we plan to migrate the UI of States into this one in order to have a single user experience from start to finish. | 1.9.0 |
| States | This is dFakto’s Orchestrator. This application is based on the AWS Step Functions specification. It allows users to create workflows (named state machines) to execute and schedule all the processes required to operate a dataFactory | 2.3.0 |
| States UI | This is the user interface of States. This interface allow the user to orchastrate the different workflows to move the data from the source system, into the data warehouse and push it to end-usage tools | 1.0.0 |
| Workers (beVault) | The workers are a piece of code that can be called by States (or AWS step functions) to execute a specific task. It also contains the Stores, which are connectors to different endpoints (databases, Excel files, FTP, directories, …). Those stores can be used inside a worker to access and manipulate data. | 1.11.2 |
Components' interactions
The user can access beVault through their browser. There are currently two distinct interfaces for beVault, one for Metavault, the modeler and one for States, the orchestrator.
beVault UI calls the API of metavault or states to handle user requests.
Several database servers can be configured in metaVault during the installation. MetaVault can either create a new database or use an existing one, which is called an environment. MetaVault, thanks to its embedded SQL Engine, will manage (create, update, delete) the tables in an environment to generate the Data Vault based on the implementation done in the interface.
When the user deploys a new version, metaVault will generate some state machines to operate beVault (one per data package to load the data from staging to the raw vault, one per snapshot, …)
metaVault contains some workers to be able to load the data from the staging to the raw vault. Those workers are being called by the state machine automatically generated (CFR 4). The workers frequently call States to know if some work is expected of them.
metaVault and States use an OAuth2 identity server to manage the login of users. This way, the application can use an SSO (Single Sign On) and doesn’t have to manage passwords, etc.
The workers ask States frequently to know if there is a job to do. When it's the case, the worker executes its code with the parameters it receives from States and sends back the output. Those workers can either be deployed next to the rest of the components or directly on the client’s infrastructure to avoid having to expose databases or other systems to the internet.
Stores (Stores ) can be configured to access external data sources. Those stores can be used by the workers to extract or manipulate data from external endpoints.
States uses Redis to manage the queues of executions of state machines.
It is possible to use AWS Step Functions instead of States to operate beVault. The state machines will be automatically generated in AWS and the workers can also be used to execute some tasks
